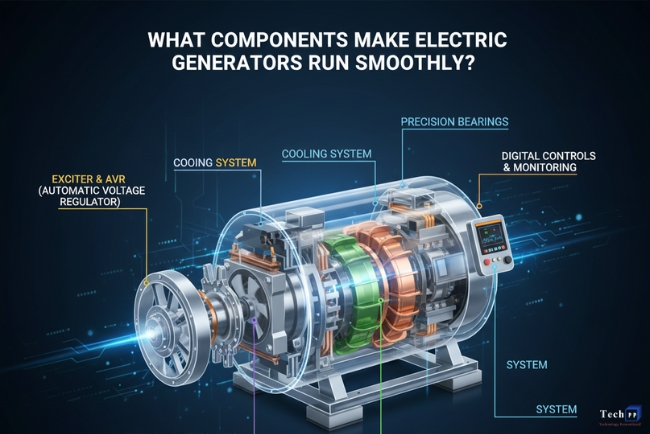
Electric generators are at the heart of modern power systems, transforming mechanical energy into electrical energy that fuels homes, businesses, and industries. Every part of a generator works together to ensure steady, reliable performance. When maintained properly, these machines can operate efficiently for decades, keeping essential systems powered.
A crucial component that plays a major role in performance is the electric generator stator, which, along with other vital parts, helps maintain balance, consistency, and output quality. Understanding how each section contributes to the overall operation allows engineers and users to appreciate the complexity behind seamless energy generation.
The Role of the Stator in Power Generation
The stator acts as the stationary part of a generator’s electrical system. It contains coils of wire wound around a metal core. When the rotor spins inside it, a magnetic field interacts with the coils to create an electric current.
The electric generator stator must remain strong and precisely aligned to ensure efficient energy conversion. Any irregularities can cause voltage fluctuations or mechanical stress. High-quality materials and precision engineering help the stator withstand heat and pressure while maintaining consistent performance.
The Rotor and Its Rotational Motion
The rotor is the moving component that generates the magnetic field necessary for electricity production. It is mounted on a central shaft and spins at high speeds, driven by an external energy source such as steam, wind, or water turbines.
Proper rotor balance ensures smooth rotation and reduces vibration. Bearings and alignment systems keep the rotor centered within the stator, preventing friction or wear. Together, these components enable efficient interaction between motion and magnetism, the core principle behind electricity generation.
Bearings That Ensure Mechanical Stability
Bearings are small but vital parts that keep the rotor spinning smoothly. They reduce friction and support the shaft under high rotational pressure. Without well-maintained bearings, generators experience vibration, noise, and performance loss.
Modern generators use lubricated or magnetic bearings for minimal resistance and extended service life. These components help maintain mechanical harmony, ensuring the generator operates quietly and efficiently. Regular inspection and lubrication prevent premature wear and costly downtime.
Cooling Systems That Regulate Heat
As generators produce electricity, heat builds up inside the system. Cooling mechanisms prevent overheating and protect sensitive parts from damage. Depending on design, generators use air, hydrogen, or water cooling to maintain optimal temperatures.
Efficient cooling extends component life and preserves insulation quality around coils. It also minimizes performance drops during continuous operation. A well-regulated temperature system is key to preventing breakdowns and sustaining an uninterrupted energy supply.
Voltage Regulators That Balance Output
A generator must provide consistent voltage regardless of load changes. Voltage regulators control the output, adjusting the excitation current to maintain stability. This keeps lights, equipment, and machinery operating safely and efficiently.
Advanced regulators include automatic systems that respond instantly to demand fluctuations. They protect electrical devices from surges and dips, reducing the risk of system failure. Reliable regulation ensures energy remains steady under varying operational conditions.
Lubrication Systems That Reduce Wear
Friction is one of the biggest enemies of mechanical performance. Lubrication systems distribute oil evenly across moving parts, minimizing metal-to-metal contact. This process prevents overheating and extends the lifespan of internal components.
Proper lubrication also reduces noise and energy loss caused by frictional resistance. Automated oil circulation systems in modern generators help maintain constant lubrication levels, ensuring continuous operation without frequent maintenance interruptions.
Control Panels That Manage Performance
Control panels act as the command center for generator operation. They monitor performance metrics like voltage, current, and temperature. Operators use these panels to start, stop, and adjust generator functions as needed.
Modern systems feature digital displays and safety alarms that alert technicians to potential issues. Control panels also provide automatic shutdown functions in case of faults, protecting both the machine and connected equipment.
Frames and Casings That Provide Structure
The frame or casing forms the structural backbone of a generator. It holds all components in place and protects them from dust, moisture, and physical damage. Durable materials like steel or aluminum alloys are used for strength and corrosion resistance.
Beyond protection, the casing also contributes to noise reduction and vibration control. Properly designed frames support internal alignment, ensuring all mechanical and electrical elements function as a unified system.
Also Read : Sintterikytkin: The Future of Power Transmission
Essential Maintenance Practices for Long-Term Efficiency
To keep generators running at peak performance, it’s important to:
- Inspect bearings and lubrication levels regularly
- Clean the cooling system and replace filters when needed
- Check voltage regulators for proper function
- Monitor alignment between rotor and stator
- Tighten loose connections and inspect insulation integrity
These simple but vital steps extend generator life and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Smooth generator performance depends on the coordination of multiple parts, each with its own essential function. From the rotor’s motion to the electric generator stator’s stability, every detail ensures steady power output and mechanical efficiency.
Regular maintenance, high-quality materials, and precise engineering form the backbone of reliable energy generation. When all components work together seamlessly, generators deliver consistent power that keeps industries, offices, and homes running without interruption.