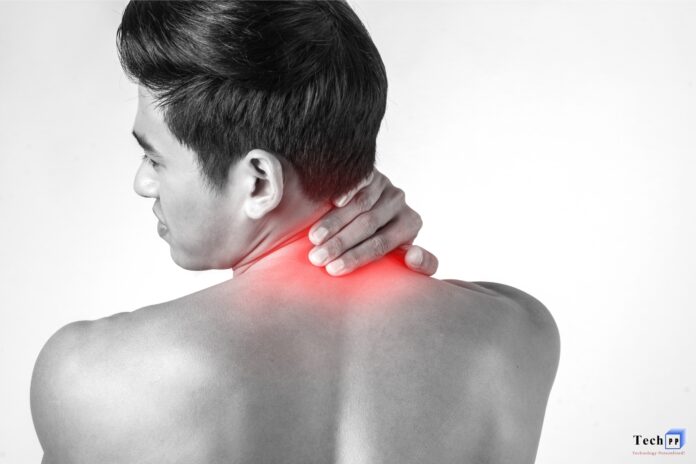
This guide will examine inomyalgia , a chronic pain condition which affects many people around the world. Although it does not receive as much attention as many other pain disorders, it is being studied more closely and greater recognition is being given to its symptoms, potential underlying conditions, and approaches to treatment.
Introduction to Inomyalgia
Inomyalgia is defined as a chronic condition where the individual suffers from muscle pain and persistent soreness. This condition is not the result of muscle overexertion or injury. Instead, inomyalgia is a variable and ongoing pain condition. Inomyalgia pain is very common and many people experience it with day to day activities as well as with work.
Inomyalgia in some way is similar to fibromyalgia. Inomyalgia is unique unto itself and in many ways requires different understanding and treatment.
Key Symptoms
Inomyalgia is identified with the following symptoms:
- Muscle pain and different soreness which includes different and overlapping with numerous muscle groups.
- Inactivity of different muscle groups for a period of time and as upon waking.
- Chronic exhaustion of the body which does not respond to rest.
- Inomyalgia does have its own unique symptoms however many inomyalgia suffers tend to have difficulty with sleep as well.
- Cognitive Fog – Difficulty focusing known as “brain fog.”
The flare-ups are most often the result of stress, a change in weather, physical activity, or even becoming sick. Symptoms seem to flare up in a different manner each day.
Possible Causes
Inomyalgia is a condition in which the exact cause is yet to be identified. However, there are multiple factors that are being studied:
- Factors in the Nervous System – The way the nervous system processes signals of pain may undergo change.
- Microtrauma – The repeated little damage that i s caused to the muscle s’ fibers.
- Inflammation of the muscles – A possible cause of pain may be low level of inflammation.
- Hormones that are out of balance – Changes in stress-related hormone, Cortisol may cause irregularities.
- Familial Altered Definition – Increased risk of suffering from chronic pain can be attributed to a family history of pain disorders.
Inomyalgia is most likely a combination of the factors mentioned above.
Diagnosis
Inomyalgia is a relatively recent term in the medical literature, which makes diagnosis difficult. No single laboratory test is available to confirm this condition. Medical practitioners rely on:
- Medical Records – The collection of evidence that documents the medical history and the duration and severity of symptoms presented.
- Physical Examination – Observing the tenderness and the range of motions of the muscles.
- Erasure of Other Medical Ailments – Eliminating diseases such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, or myopathy.
To attain the diagnosis, symptoms are required to persist for months and have a substantial impact on day to day activities.
Treatment Approaches
While inomyalgia doesn’t have a cure, a blend of treatments can assist in improving symptoms and help restore the individual’s quality of life.
1. Medications
- Pain relievers – Minor pain can be treated with over-the-counter acetaminophen or NSAIDs.
- Muscle relaxants – Effective in decreasing rigidity and spasms.
- Prescription pain modulators – Some antidepressants and anticonvulsants have been found effective for nerve pain and can be prescribed.
2. Physical Therapy
Improved mobility can be achieved with gentle strengthening and stretching, as well as posture training, which helps decrease muscle tightness.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Balanced diet – Omega-3 and high antioxidant foods can help decrease inflammation.
- Regular low-impact exercise – Swimming, yoga, and walking.
- Sleep hygiene – Maintaining a sleep schedule helps in reducing fatigue.
4. Stress Management
Mindfulness and meditation, as well as deep breathing, can help diminish stress-related flare-ups.
Living With Inomyalgia
Living with inomyalgia often means changing lifestyles and living with managing a blend of activity and rest. Patients can benefit from:
- Pacing – Achieving tasks in stages to avoid overexertion.
- Support networks – Online and local support groups for shared tips and info.
- Regular medical check-ups – Active monitoring of symptoms and changing treatments as necessary.
Working proactively to put a multidisciplinary strategy in place can tend to offer the most positive long-term results.
Research and Future Outlook
The examination of Inomyalgia seems like it will be happening for a long time. With specific inomyalgia clinics opening, it is likely that more research will be done to understand it more in depth and also to improve treatment options. Early recognition by healthcare professionals can lead to a definitive diagnosis, and Inomyalgia can be managed more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Inomyalgia and fibromyalgia, what are the differences?
A: Both of inomyalgia and fibromyaglia involve pain in the muscles and other body parts, but inomyalgia seems to be linked with specific muscles with specific patterns of muscle involvement which causes it, and with possible other underlying causes. Inomyalgia is fibromyalgia’s precursor.
Q2: Inomyalgia: To what extent is it curable?
A: There is currently no known diagnosis, but lifestyle changes and therapy seem to really help many patients manage their life a little easier.
Q3: What is the effect of inomyalgia and exercise and what is the best exercise to do to improve it?
A: Inomyalgia and exercise have a strengthening and curative effect on each other, with swimming being the best form of exercise. With gentle yoga exercises and swimming being the best forms of gentle exercise, Inomyalgia yoga and regular walking can greatly improve the muscle tone and also greatly improve health.
Q4: What are the inomyalgia symptoms and what can trigger flareups?
A: All the inomyalgia symptoms and other body parts are common triggers of overexertion, taking poor unmedicated sleep, lack of sleep, weather changes, and stress, and trigger flare-ups of fibromyalgia.
Q5: Can inomyalgia be diagnosed by a general practitioner?
A: Diagnosis by general practitioner, and by other healthcare professionals who have a specific background in the heathcare system and diagnosis can sometimes also do the diagnosis too.
Q6: Can eating nutritionally affect the inomyalgia symptoms?
A: Though patients suffering from inomyalgia do not have a diet to help their pain, following a holistic diet is likely to help manage pain like other forms of holistic and anti-inflammatory foods.
Final Thoughts
Inomyalgia intricate chronic pain condition that needs more awareness both publiclyand medical wise. Knowing its symptoms, potential triggers, and treatment options enable both patients and medical personnel to collaborate towards improved daily functioning. Even with some difficulties, persistent investigations provide promise for more effective treatment alternatives later on.